Types of Electrical License & its Eligibility Criteria
-
Sapna
- May 3, 2024

Various types of licenses are required in the field of electrical work to ensure that professionals are qualified and competent to perform electrical installations, maintenance, and repairs safely and effectively.

Regulatory bodies typically issue these licenses, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction. They serve as a formal credential validating an individual’s ability to comply with electrical codes and standards. In this blog, let’s explore different types of electrical licenses and their eligibility criteria.
Table of Contents
Types of Electrical Licenses & their Eligibility Criteria
Electrical licensing ensures that professionals are adequately trained and qualified to perform electrical work safely and competently. Here’s a detailed look at three specific types of electrical licenses: Contractor, Supervisor, and other licenses that might be available depending on regional regulations.
Contractor Electrical License
The Contractor Electrical License is a crucial credential for businesses and individuals planning to offer electrical services professionally. This license allows the holder to legally contract and perform electrical installation, repair, and maintenance services. It is typically required for those who wish to operate their own electrical contracting business or manage large-scale electrical projects.
Subcategories of Contractor Electrical License
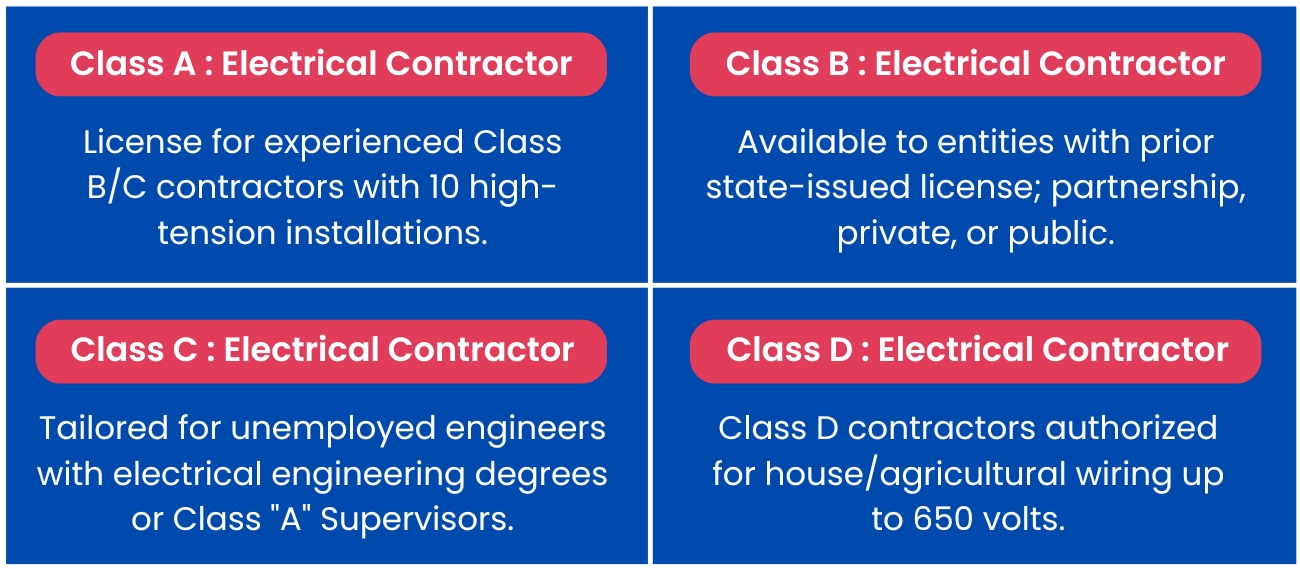
Depending on the authority and specific regulations, the Contractor Electrical License may be categorised into several types, reflecting the scope and scale of work the licensee is authorised to perform. Here are some common subcategories:
1. Class A Electrical Contractor Eligibility Criteria:
- This license is intended for individuals or legal entities (partnerships, proprietorships, or companies) with at least three years of experience as a Class B or C contractor.
- They must have successfully executed at least ten high-tension installations.
- Individuals or firms’ partners should have at least five years of experience in electrical operation and maintenance.
- Holders of an existing license from another state with at least three years of experience managing electrical works above 33kv, including the successful execution of 10 high-tension installations, are also eligible.
2.Class B Electrical Contractor Eligibility Criteria:
- Available to any individual or legal entity (partnership firm, private or public limited firm).
- The applicant must already possess a license issued by a competent state authority.
3.Class C Electrical Contractor Eligibility Criteria:
- This class is tailored for unemployed engineers holding degrees or diplomas in electrical engineering or for Class “A” Supervisors.
4.Class D Electrical Contractor Eligibility Criteria:
- Suitable for individuals holding a certificate or permit as a supervisor or wireman issued by the office of the chief/senior electrical inspector.
- Class D contractors are authorised to undertake house and agricultural wiring up to 650 volts.
Supervisor Electrical License
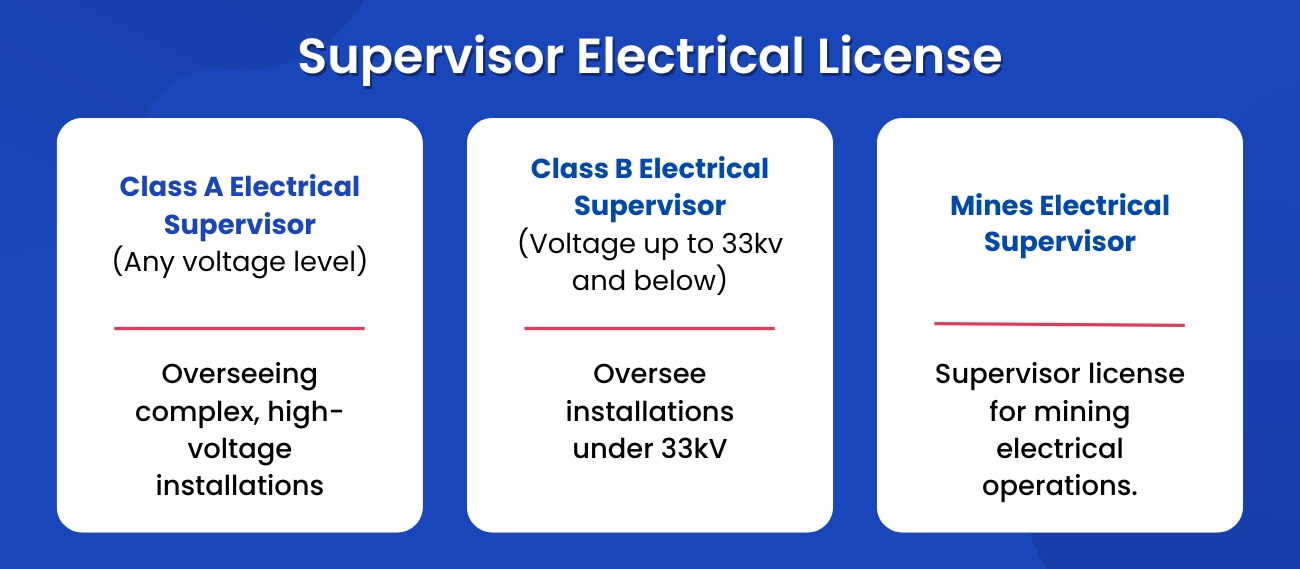
An Electrical Supervisor License is generally required for individuals supervising electrical work. This license ensures that installations are safe, meet regulatory standards, and are carried out efficiently. These licenses can be categorised into different classes based on the voltage levels of the installations supervised and the specific environments in which the work is conducted.
Here’s a detailed look at each class and their eligibility criteria:
1.Class A Electrical Supervisor (Any voltage level)
A Class A Electrical Supervisor is authorised to supervise electrical work on systems of any voltage level. This license is typically required for overseeing complex and high-voltage installations in various settings, including industrial, commercial, and residential projects.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Educational Qualification: Typically, a degree or diploma in Electrical Engineering from a recognised institution.
- Experience: Extensive experience in handling high-voltage electrical systems, usually 5 to 10 years, depending on the issuing authority.
- Testing: Passing a comprehensive examination that covers all aspects of electrical safety, code compliance, and system design for any voltage level.
2. Class B Electrical Supervisor (Voltage up to 33kv and below)
A Class B Electrical Supervisor is qualified to oversee electrical installations and maintenance on systems that operate at or below 33 kilovolts. This class is suited for supervisory roles in lower voltage environments such as smaller industrial units, residential complexes, and commercial buildings.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Educational Qualification: A diploma or degree in Electrical Engineering or a related field from a recognised institution.
- Experience: Experience requirements are generally less stringent than Class A, often around 3-5 years, focusing on systems with voltages up to 33kv.
- Testing: A qualifying exam that tests knowledge and skills pertinent to managing and supervising electrical installations and maintenance for voltages up to 33kv.
3.Mines Electrical Supervisor
This license specialises in supervisors who oversee electrical operations in mining environments. These settings pose unique challenges due to explosive gases, dust, and other hazardous conditions, necessitating stringent safety standards.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Educational Qualification: Applicant needs to have a degree or diploma in Electrical Engineering, often with a specialisation or additional certification in mining electrical systems.
- Experience: Specific experience in mining operations, dealing with the unique electrical systems used in mining environments. The required duration can vary but typically involves several years of relevant experience.
- Testing: Passing an examination that covers mining safety regulations, electrical standards applicable to mines, and practical knowledge of managing electrical operations in mines.
Residential Electrical

Residential electrical work involves the activities like installation, maintenance, and repair of electrical systems and components in residential buildings. This includes wiring, outlets, switches, lighting, and other electrical fixtures. Electricians need to ensure that all the electrical systems are safe, efficient, and comply with electrical codes and standards. The work might also involve upgrading existing electrical systems, installing smart home technology, and troubleshooting electrical problems.
Eligibility Criteria for Residential Electrical
- Education: A high school diploma or equivalent is usually required. Some level of technical training, often obtained through a vocational school or community college, is highly beneficial.
- Apprenticeship: Many electricians start their careers with training, which combines on-the-job training with classroom instruction. This usually lasts about 4-5 years.
- Licensing: Most states and localities require electricians to be licensed. The requirements for licensing include passing a required exam that tests knowledge and skills of electrical theory, local electric, and building codes.
- Continuing Education: Electricians must often complete continuing education courses to keep their licenses valid and updated with changes to the National Electrical Code and other standards.
- Physical Ability: Residential electrical work can be physically demanding. Electricians must often operate in small spaces, climb ladders, and lift heavy materials.
Other Electrical Licenses
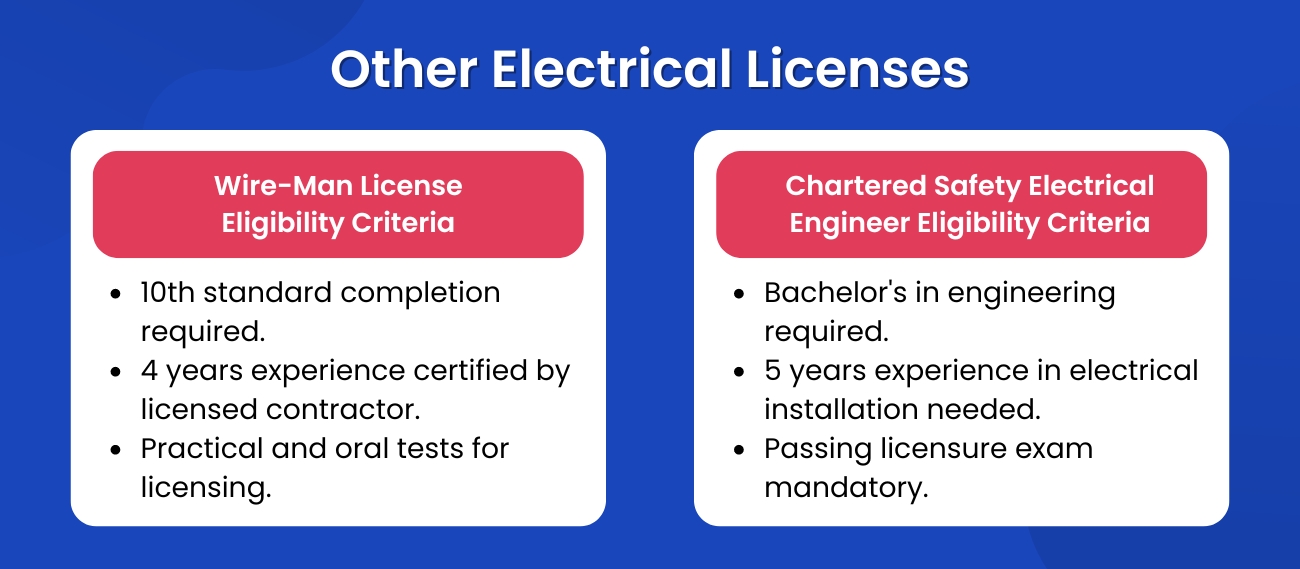
There are many other specialised Electrical licenses, such as the Wire-Man License, which allows individuals to work on residential and small commercial electrical systems, and Chartered Safety Electrical Engineer, which focuses on safety management and compliance in electrical operations. Each license has specific eligibility requirements, which includes:
Wire-Man License Eligibility Criteria:
- Applicants must have completed the 10th standard.
- They should have at least four years of experience, certified by a licensed electrical contractor.
- The examination process involves practical tests on machine connections and wiring installations and an oral test covering the entire syllabus. Candidates need to achieve a minimum score to pass and receive their license.
Chartered Safety Electrical Engineer Eligibility Criteria:
- This role requires a bachelor’s degree in engineering.
- Candidates must have at least five years of experience in electrical installation operation and maintenance.
- They must pass a specific examination to become licensed, which may include knowledge of safety regulations, electrical codes, and first aid related to electrical engineering.
Conclusion
Obtaining the proper electrical license is essential for electrical industry professionals, as it ensures they meet the required standards of competence and safety. Every license serves specific roles governed by stringent eligibility criteria, including educational qualifications, relevant experience, and successful examination results. These licenses not only validate the capabilities of electrical professionals but also ensure that electrical installations and maintenance are conducted safely and efficiently, protecting both the workers and the public.
Match all the requirements for the smooth execution of your construction projects. Also, try adopting Powerplay, India’s best construction management software. It helps to enhance the efficiency of your projects by offering robust tools for managing all aspects of construction projects effectively, ensuring better coordination, compliance, and cost management. Download the app now and start building your dream project.