Work Breakdown Structure in Construction Management
-
 Sapna
Sapna
- June 30, 2024

Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in construction management is pivotal in meticulously organising complex undertakings into manageable components. The WBS enhances planning precision, resource allocation, and progress tracking by systematically breaking down project scope and deliverables into hierarchical levels.

This blog explores the fundamental concept of the construction WBS, its types, benefits, and practical applications within the construction industry. Discover how this structured approach fosters clarity, collaboration, and efficiency, ensuring projects stay on course amidst challenges and complexities.
Table of Contents
What Is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?

A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a project management tool that decomposes a project into smaller, more manageable components. It organises the project’s scope and deliverables into a hierarchical structure, breaking the work into tasks, sub-tasks, and work packages.
The WBS identifies all project elements, providing a clear framework for project planning, execution, and monitoring. Each level represents a finer level of detail, helping project managers and teams understand the project’s scope, allocate resources, and track progress effectively.
Why Use a WBS In Project Management?

Using a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in project management offers several key benefits:
Enhanced Project Organisation:
A WBS breaks down complicated projects into smaller, manageable tasks, allowing project managers to oversee all aspects systematically. This hierarchical structure ensures all necessary components are identified and organised efficiently.
Improved Resource Allocation:
A WBS helps allocate resources effectively by clearly outlining all project tasks. This includes estimating costs, setting timelines, and managing capacities, thereby enhancing the overall planning and execution of the project.
Better Risk Management:
A detailed breakdown of tasks identifies potential risks early, allowing for proactive management and mitigation. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected issues derailing the project.
Enhanced Team Collaboration:
A WBS facilitates better communication among the project team members by providing a clear overview of the project and task responsibilities. This clarity helps coordinate efforts across different departments and teams, improving overall collaboration.
Accurate Progress Tracking:
Project managers can track progress more accurately by having a detailed structure and project schedule, ensuring that each task is completed on time and within scope. This helps maintain control over the project and make necessary adjustments.
Clear Project Scope Definition:
A WBS forces the the project manager and team to define the project scope in detail, ensuring that all necessary tasks are included and nothing is overlooked. This precision helps in setting realistic expectations and objectives.
Why is the Work Breakdown Structure crucial to construction?
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is crucial to construction projects because it organises the construction project into manageable sections, ensuring all tasks are clearly defined and systematically planned.
This hierarchical structure aids in resource allocation, risk management, and progress tracking, which is essential for complex construction projects. By breaking down the project into smaller actionables, the WBS enhances communication and coordination among various teams, ensures accurate budgeting and project scheduling throughout, and helps identify potential issues early, leading to more efficient and effective project management.
Types of WBS
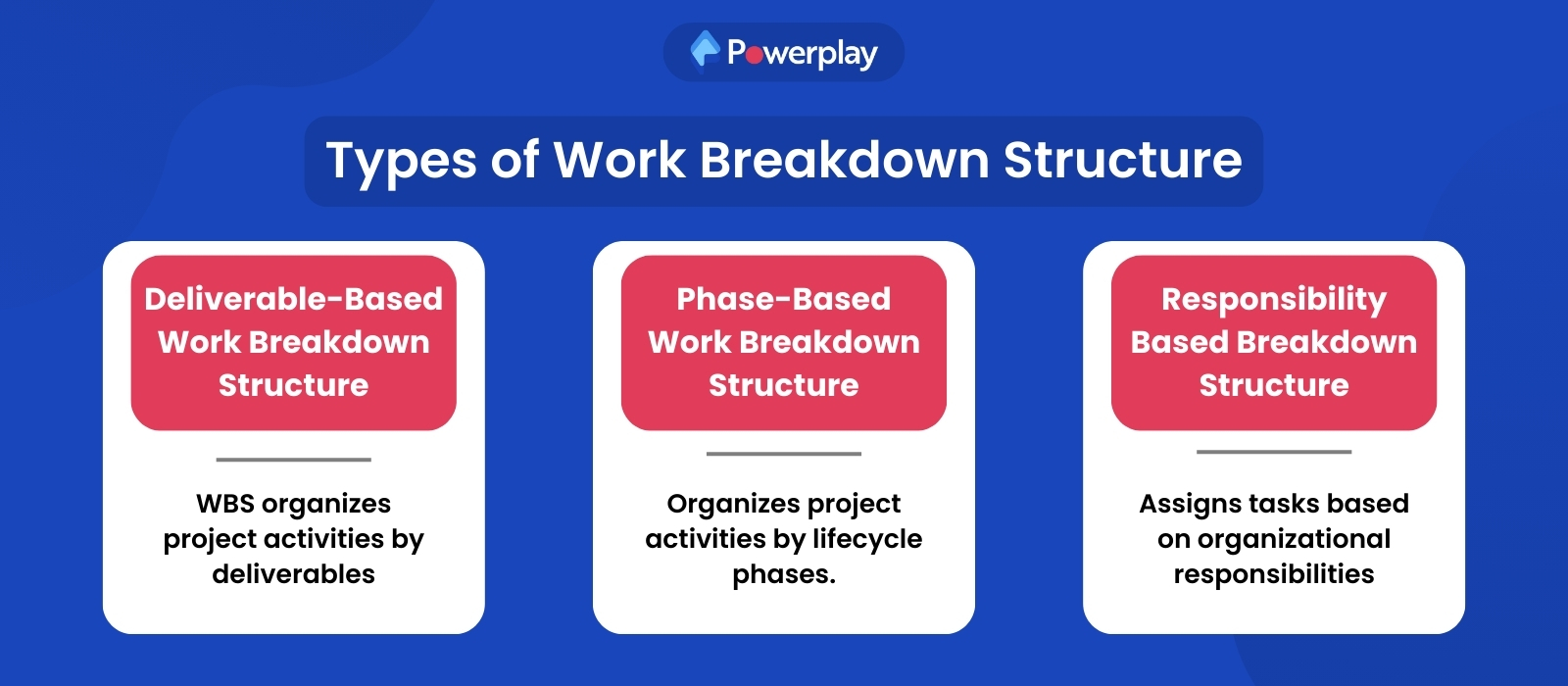
Types of WBS help organise and manage complex projects by providing a clear framework for planning, executing, and monitoring project tasks. There are three main types of Work Breakdown Structures (WBS)
Deliverable-Based Work Breakdown Structure:
This type of WBS project management organises project activities based on the project’s deliverables. Each deliverable is broken down into smaller components until manageable work packages are identified. This structure helps ensure that all deliverables are accounted for and that each piece of work contributes to the final product.
Phase-Based Work Breakdown Structure:
This phase-based WBS arranges project activities according to the project lifecycle phases, such as initiation, planning, execution, and closure. Each phase of project management institute is subdivided into tasks and sub-tasks, making managing and monitoring progress through each project stage easier.
Responsibility-Based Work Breakdown Structure:
In this structure, project activities are assigned based on the responsibilities of different organisational units or team members. It emphasises who is responsible for what work, ensuring clear accountability and efficient resource allocation.
Types of WBS Charts
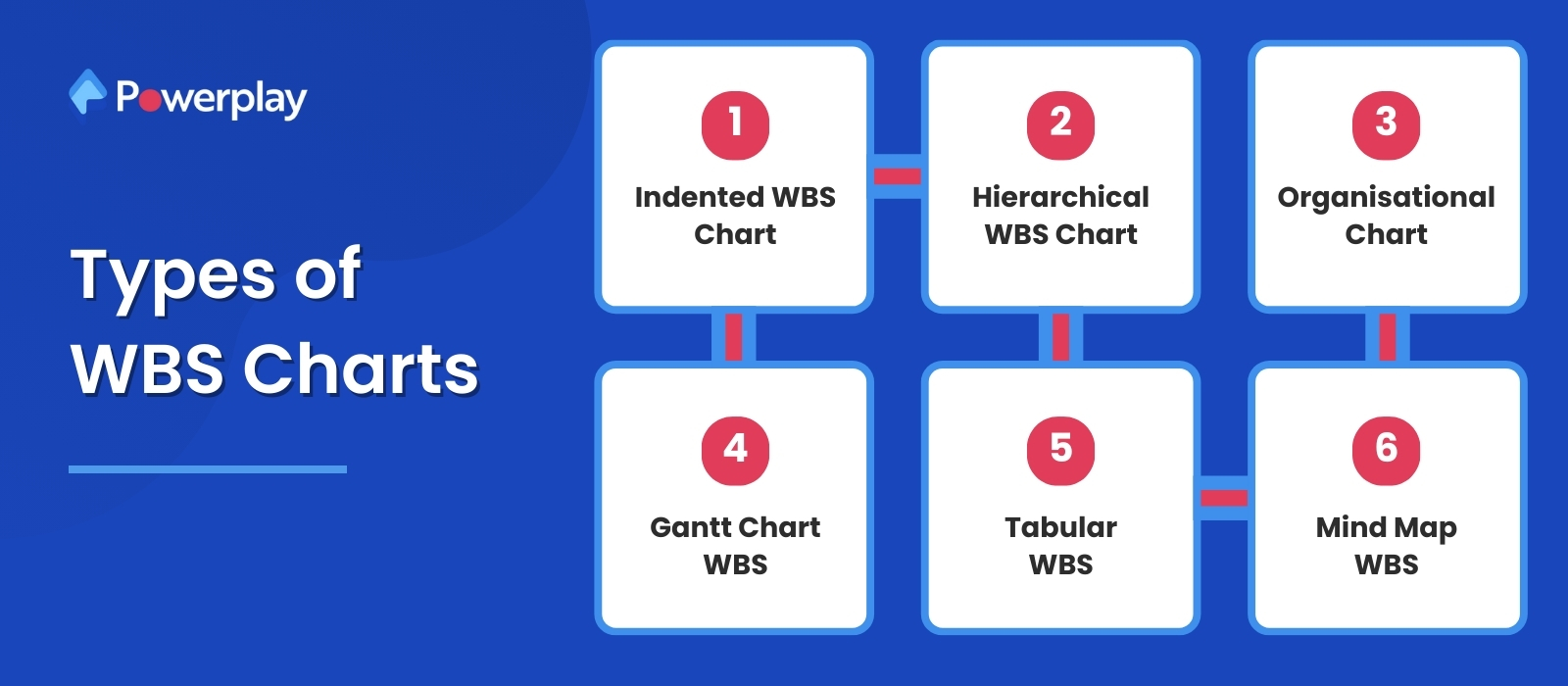
Work Breakdown Structures (WBS) can be visualised in various charts, each serving specific purposes in project management. Here are the common types:
Indented WBS Chart:
The most traditional and widely used type presents the project’s hierarchical structure in a text-based outline format. Each hierarchy level is indented under its parent level, showing the relationship between phases, deliverables, and tasks.
Hierarchical WBS Chart:
Similar to the indented chart but presented graphically, this type uses a tree-like structure to illustrate the breakdown of project components. It visually displays the parent-child relationships between project phases, deliverables, and work packages.
Organisational Chart:
Also known as a tree diagram, this type of WBS chart resembles an organisational chart with boxes or nodes representing project phases, deliverables, and tasks. It emphasises the reporting structure and hierarchy within the project.
Gantt Chart WBS:
Integrates the WBS with a Gantt chart, visually representing project tasks over time. It links the tasks defined in the WBS to their scheduled timelines, helping plan and schedule project activities.
Tabular WBS:
Presents the WBS in a tabular format, typically used for detailed breakdowns in project management documents where each row represents a specific task or work package. Columns may include task descriptions, responsible parties, start and end dates, and other relevant details.
Mind Map WBS:
A visual representation that uses branches radiating from a central idea or theme is often used for brainstorming and organising ideas. It can be adapted to depict project phases, deliverables, and tasks in a non-linear format.
How to Create a Work Breakdown Structure In Six Steps
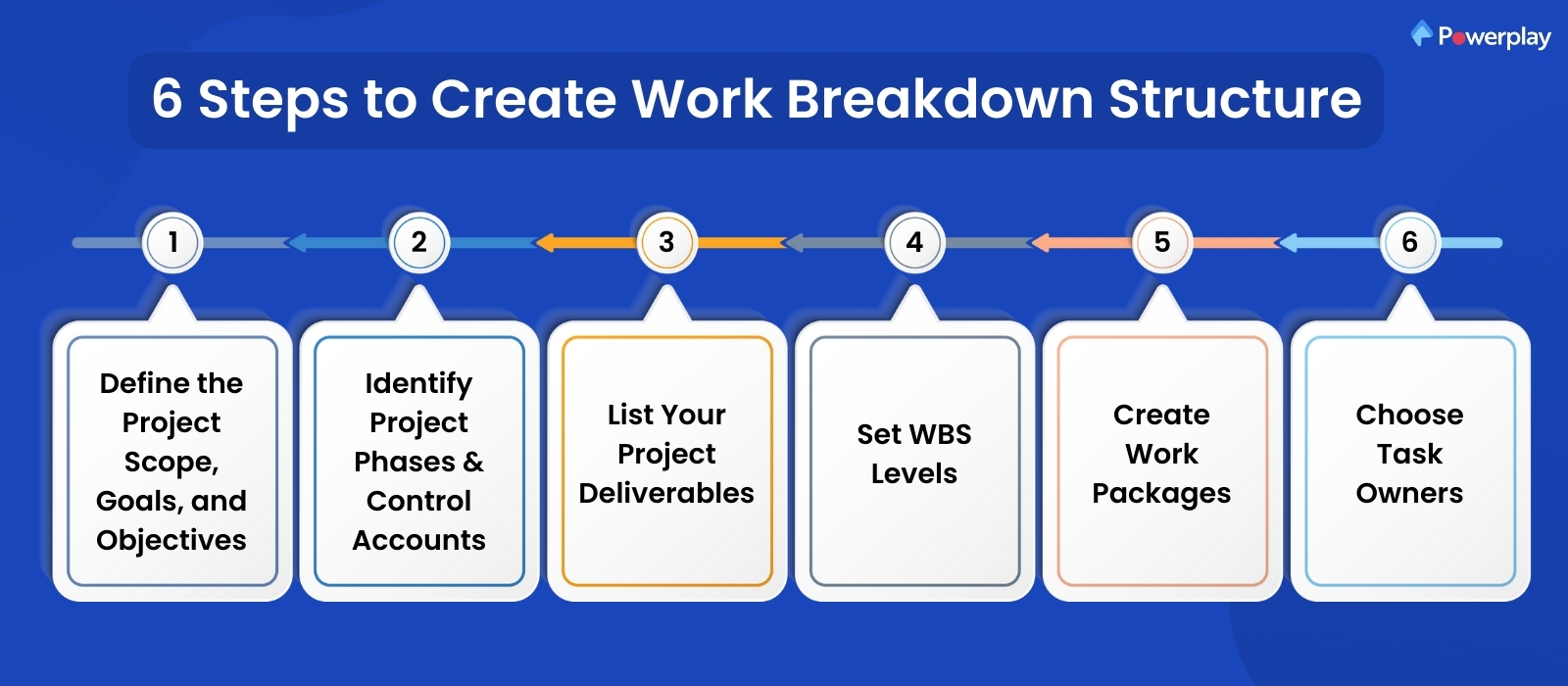
Making a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is crucial for effectively managing projects, especially in construction and other complex industries. Here are detailed steps to create a WBS:
Define the Project Scope, Goals, and Objectives:
Start by clearly defining the project charter, what the project aims to achieve, its scope, and the specific goals and objectives. This step sets the base for the entire project structure.
Identify Project Phases & Control Accounts:
Break down the project into phases or major stages. Each phase of project plan should represent a significant milestone or deliverable. Control accounts are used to manage costs and resources for each phase.
List Your Project Deliverables:
Identify and list all the deliverables that must be produced to complete the project successfully. These are tangible outcomes or results that stakeholders expect from the project.
Set WBS Levels:
Organise deliverables into hierarchical levels. Start with the highest level (level 1) representing the entire project, then break it down into smaller, more manageable components (levels 2, 3, and so on) until you reach the lowest level work packages.
Create Work Packages:
Define work packages and the smallest work units within the WBS. Each work package should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They should also have clear boundaries and be assigned to a single or small team member.
Choose Task Owners:
Assign each work package to a responsible team member or task owner. This guarantees accountability and provides clarity regarding responsibilities for each task or work package.
When to Use a WBS?
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in construction management is a valuable project management tool suitable for various scenarios where project complexity requires detailed planning and organisation. Here are key situations when a WBS is particularly useful:
- Complex Projects: Use a WBS for projects with multiple phases, diverse stakeholders, and intricate dependencies between tasks.
- Large-Scale Projects: It helps manage large-scale projects by breaking them down into manageable components, making allocating resources and tracking progress easier.
- Scope Definition: Use it to clearly define and communicate the project scope, ensuring all stakeholders understand what will be delivered.
- Project Planning: It facilitates detailed project planning by organising tasks and deliverables into hierarchical levels, aiding in resource allocation and scheduling.
- Risk Management: A WBS helps identify potential risks early in the project lifecycle by breaking the project into smaller, identifiable elements.
- Cost Estimation: It supports accurate cost estimation and budgeting by providing a structured framework to allocate costs to specific tasks and work packages.
Work Breakdown Structure Best Practices

Creating an effective Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) involves following best practices to ensure clarity, efficiency, and successful project management. Here are five key best practices:
Involve Stakeholders:
Engage key stakeholders, including clients, team members, and subject matter experts, in the WBS development process.Their input ensures alignment with project goals, enhances buy-in and improves the accuracy of task identification and sequencing.
Use Hierarchical Structure:
Organise the WBS hierarchically, from the highest level (project phase or major deliverable) to the lowest level (individual work packages). This structure provides a clear breakdown of project components, facilitating easier project management body, and understanding.
Focus on Deliverables:
Define deliverables clearly and precisely at each level of the WBS. Each level should represent a distinct deliverable or milestone contributing to the project objectives. This clarity helps set expectations and monitor progress effectively.
Keep it Manageable and Detailed:
Strike a balance between granularity and manageability. Ensure that each work package is sufficiently detailed to be actionable and assignable to a specific team member or group. Avoid making levels too detailed or high-level, leading to confusion or oversight.
Review and Refine Regularly:
Review and refine the WBS regularly throughout the project lifecycle. As the project progresses, updates may be necessary to accommodate scope, resources, or priorities changes. This iterative process ensures that the WBS remains relevant and effective in guiding project execution.
Why you need to get the team involved in the work breakdown structure creation
Involving the team in creating the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is crucial for several reasons. First, it fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among team members, enhancing their motivation and accountability throughout the project.
Second, team input ensures that tasks are accurately identified and sequenced based on their expertise and understanding of project requirements, reducing the risk of overlooked details or misaligned expectations.
Lastly, collaborative WBS development promotes better communication and coordination, aligning team members on project goals and milestones from the outset, which improves overall project efficiency and success rates.
Tips for Creating a Strong Work Breakdown Structure
Creating a strong Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in construction management is essential for effective project management. Here are five main tips to achieve this:
- Start with Clear Objectives: Define the project objectives and scope clearly to ensure that the WBS aligns with the project’s goals.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage stakeholders, including clients and team members, to gather input and ensure comprehensive coverage of project deliverables.
- Use Hierarchical Organisation: Structure the WBS hierarchically from major project phases to detailed work packages to improve organisation and clarity.
- Focus on Deliverables: Define deliverables at each level of the WBS to clearly outline what needs to be achieved. This will help set milestones and track progress.
- Review and Iterate: Regularly review and refine the WBS as the project evolves to accommodate changes and ensure it remains relevant and effective.
What WBS challenges can you expect?

Creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in construction management can present several challenges, including:
Scope Definition: Difficulty accurately defining project scope, which can lead to incomplete or unclear WBS elements.
Hierarchy Complexity: Managing the balance between granularity and complexity in the hierarchical structure of the WBS, ensuring it remains manageable yet detailed.
Stakeholder Alignment: Ensuring alignment among stakeholders regarding project objectives, deliverables, and the full-work breakdown structure in construction management of work packages.
Scope Changes: Handling changes in project scope or requirements may necessitate revisions to the WBS to reflect updated deliverables and tasks.
Resource Allocation: Challenges in accurately estimating and allocating resources to each work package based on the WBS breakdown.
Integration with Project Management Software: Integrating the WBS effectively with project management tools or software, ensuring consistency and compatibility throughout project execution.
WBS Software
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) software plays a vital role in effective construction management by providing a structured framework to break down complex projects into manageable tasks and identify project deliverables beforehand. It helps construction managers allocate resources efficiently, track project progress against milestones, and manage dependencies between tasks, maintaining project timelines and budget adherence.
Must-Have Features of WBS Software
When choosing Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) software, consider the following must-have features:
- Hierarchical Structure: The software should support creating a hierarchical breakdown of project deliverables, allowing for levels of detail from project phases to work packages.
- Task Dependencies: It should enable defining and managing dependencies between tasks or work packages, facilitating accurate scheduling and resource allocation.
- Collaboration Tools: Incorporate features such as real-time editing, commenting, and sharing capabilities to ensure team members can work together seamlessly on the WBS.
- Integration: Ability to integrate with other project management tools and software for data synchronisation, allowing seamless workflow and reporting across different platforms.
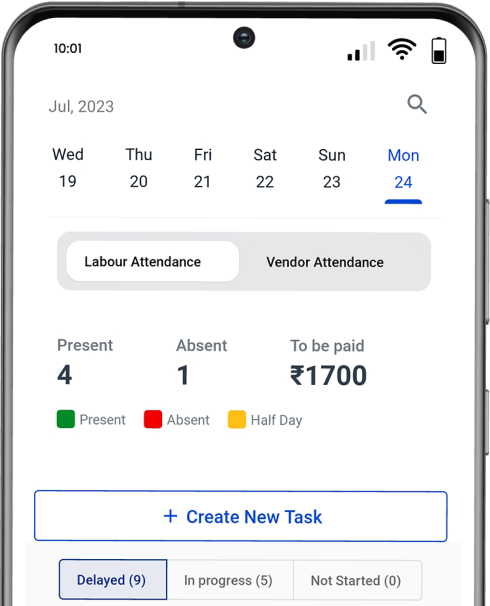
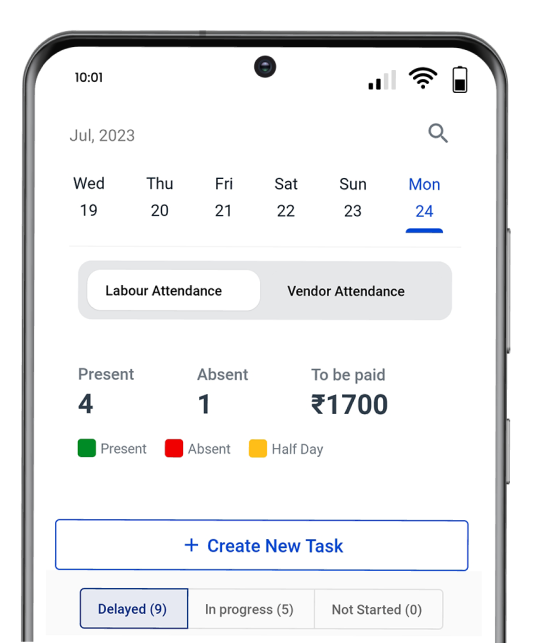
How to Create a WBS in Powerplay

Powerplay is a construction management software that offers robust tools for creating and managing Work Breakdown Structures (WBS).
Here’s how you can create a WBS in Powerplay:
Project Setup: Start by setting up your project within Powerplay. Define the project scope, goals, and objectives to establish a clear foundation.
Create Phases and Tasks: Use Powerplay to break your project into phases and tasks. Phases could include planning, excavation, foundation, superstructure, finishing, etc.
Hierarchy Creation: Organise tasks hierarchically by creating subtasks under each phase. This allows you to define smaller, manageable components contributing to the overall project.
Assign Responsibilities: For each task or subtask, assign responsibilities to specific team members. Powerplay allows you to designate task owners, ensuring accountability and clarity in project execution.
Monitoring and Reporting: Track progress report within Powerplay by monitoring task completion against the WBS. Generate reports to analyse project performance and make informed decisions.
Share

Sapna is a versatile content writer with two years of experience crafting engaging content across various platforms, including blogs, websites, social media, and newsletters. She specialises in the real estate and construction industry, creating compelling narratives that resonate with diverse audiences and enhance brand visibility and engagement.